Last Updated on January 27, 2024 by Alexander Sennuga
A topic like diabetes and bananas can be intriguing.
This is so for diabetics and prediabetics, in particular. The reason is that they are always cautious with sugary foods. Bananas and other common fruits are enjoyable to eat. Some of these other fruits are apples, watermelons, and grapes. They are naturally sweet, so they are quite tempting.
But diabetics need to be very careful when making the right choices among the fruits. Not doing so can result in blood sugar spikes, especially if the right quantity is not chosen. This post will, thus, give you all the information you need about diabetes and bananas. I am going to discuss some other common fruits as well. Stay tuned.
Diabetes and Bananas
Diabetes control for diabetics is crucial. The first thing to consider is the number of total sugars and the glycemic index (GI) of raw bananas.
How much sugar is in a banana?
The figures below say it all, including the sugar content in some other fruits.
This information will help in discussing this topic.
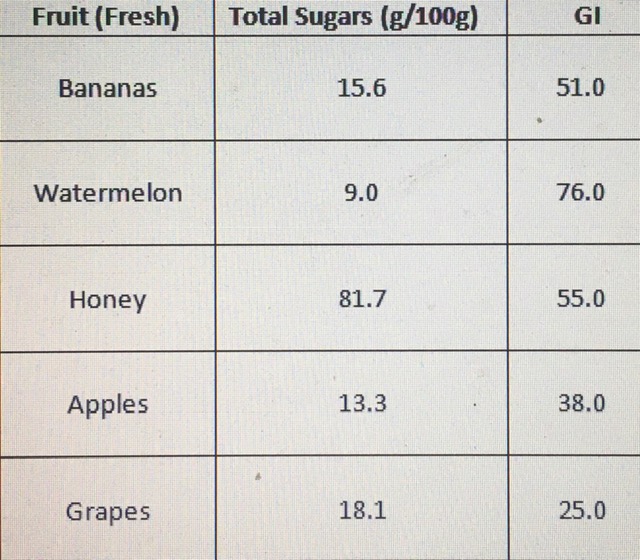
The glycemic index is a measure of how fast food would cause a spike in blood glucose. The measurement is in the range of 0 to 100.
The lower the figure, the better for diabetics and prediabetics.
A GI above 55 is considered high, and foods with that level are not recommended for diabetics.
Most high-carb foods have high GI values.
Diabetic food recipes do not contain high-GI foods.
Do bananas raise your blood sugar?
If you have diabetes, being aware of the amount and type of carbs in your diet is important.
This is because carbs raise your blood sugar level more than other nutrients, which means they can greatly affect your blood sugar management.
When blood sugar levels rise in people without diabetes, their bodies produce insulin. This helps move sugar out of the blood and into cells, where it’s used or stored.
However, this process doesn’t work as it should in people with diabetes. Instead, either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or the cells are resistant to the insulin that is made.
Without proper diabetes management, you may experience blood sugar spikes after eating high-carb foods or have constantly high blood sugar levels, both of which are unhealthy.
Source: [Healthline]
Fruits to Avoid in Diabetes
Serving size is important for all fruits, especially those high on the glycemic index. Fienman recommends thinking about the serving size of whole fruit (like an apple) to the size of a tennis ball and cutting up fruit to ½ cup. Even in these small servings, some fruits have more natural sugars and may spike blood sugar longer.
These fruits contain a high amount of natural sugar.
- mango
- banana
- papaya
- pineapple
- watermelon
Skip the canned fruit.
Canned fruits and those cute little fruit cocktail cups may be convenient and inexpensive, but they aren’t so good for you.
“Those canned in heavy or light syrup are not an ideal choice for people with diabetes,” says Kim Rose, RD, a certified diabetes care and education specialist. “This is because syrup-laden fruits contain added sugar that may be too much for the body to handle.”
Be careful with dried fruits.
Drying fruit concentrates all of the yummy fruit flavours into one smaller bite, but it also concentrates many of the sugars. Even a small amount of dried fruit can put you over the edge.
Be careful to read dried fruit labels; many of them pack added sugars. Some are even sweetened, making the sugar problem worse. If you must have dried fruit, keep the quantities small. Rose recommends dates, figs, and prunes because they are lower on the glycemic index.
Juices and smoothies can be tricky.
Many store-bought juices—orange, apple, even green juices—sneaky add extra sugars, so you’ll want to avoid those, too. Even juices or smoothies you make at home can require a lot of fruit for one glass (a small juice can often have two to three oranges), so it isn’t always the best option for people with diabetes. If you want to have a smoothie, try adding in most vegetables and something like half a banana for sweetness.
[Source: Allrecipes]
Type 2 Diabetics and Bananas
Bananas can be a healthy treat that contains plenty of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. They are cheap and widely available.
This healthy food has been shown to promote health and kidney health, stabilise blood sugar levels, and improve insulin sensitivity.
However, eating too many bananas can cause trouble for people with diabetes due to their higher carbohydrate counts, which may lead to blood sugar swings. When eaten in excess, bananas may also cause digestion issues such as bloating, gas, and an upset stomach.
They may contribute to sleepiness and weight gain, and the sweetness of bananas may contribute to dental health issues such as cavities and gum disease.
Unripe bananas have the fewest number of carbohydrates and calories and contain the highest levels of both pectin and resistant starch, while still having the high amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that ripe bananas have. This may be the best choice for people with diabetes who want to incorporate bananas into their daily diet.
Moderation is key, so if you choose to incorporate bananas into your diet, work with your doctor and/or nutritionist to find a balanced way to add this healthy fruit into your meal plan, keeping your diabetes and health goals in mind.
Source: [Diabetesstrong]
Unripe Bananas (Plantain)

Green (unripe) bananas, also known as Plantain are well-known in Africa and Asia.
They are widely consumed as food, as they are boiled, grilled, or baked to eat.
One nutritional characteristic of the product is this:
While the starch in ripe bananas has naturally been converted to sugar, the starch in plantains is resistant to starch.
This means its starch is not convertible to sugar—indigestible starch.
What is the benefit of this to diabetes patients?
Diabetics can consume this as food without fear of a spike in their blood sugar!
How about other fruits?
Let us look into some fruits like watermelon, apples, and grapes.
The reason for this is that there are other common fruits that diabetics want to enjoy.
Can I Eat Watermelon If I Have Diabetes?

Watermelon is typically a summertime favourite. Although you may want to dish some of the sweet treats up at every meal or make it your go-to summer snack, it’s important to check the relevant nutrition information first.
If you have diabetes, you know how important it is to watch what you eat and monitor your blood sugar levels.
Watermelon does contain natural sugars. Depending on your overall diet and the amount of watermelon you consume, this may have an impact on your blood sugar level.
Keep reading to learn how adding watermelon to your diet may affect you.
Should people with diabetes eat apples?

Apples are an excellent fruit to include in your diet if you have diabetes.
Most dietary guidelines for people living with diabetes recommend a diet that includes fruits and vegetables (21).
Fruits and vegetables are full of nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
In addition, diets high in fruits and vegetables have repeatedly been linked to lower risks of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer (Trusted Source22Trusted Source.
While apples are unlikely to cause spikes in your blood sugar levels, they do contain carbs. If you’re counting carbs, be sure to account for the 27 grams of carbs an apple contains.
Also, be sure to monitor your blood sugar after eating apples and see how they affect you personally.
The bottom line
Apples are a delicious and healthy food to add to your diet, regardless of whether you have diabetes or not.
Here are some tips for people with diabetes to include apples in their meal plans:
- Eat it whole. To reap all of the health benefits, eat the apple whole. A large part of the nutrient value is in the skin.
- Avoid apple juice. The juice does not have the same benefits as the whole fruit, since it’s higher in sugar and missing fiber.
- Limit your portion. Stick with one medium apple since larger portions will increase the likelihood of a blood sugar spike.
- Spread out your fruit intake. Spread your daily fruit intake throughout the day to keep your blood sugar levels stable.
[Source: healthline.com]
Can You Eat Grapes If You Have Type 2 Diabetes?

To control the rising blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes, it is necessary to monitor it continuously. Some foods help keep blood sugar levels down, including some fruit.
Type 2 diabetes is a situation in which a person’s pancreas is unable to produce sufficient amounts of insulin, causing the blood sugar level to rise. It increases the risk of heart disease and stroke if the blood sugar level is ignored or checked periodically.
Although the heart is comforting, some changes in the diet can help keep blood sugar under control. Experts also say that if you include this famous fruit in your diet, then you can control your blood sugar level.
- Experts say that the elements found in grapes can reduce blood sugar levels. A study conducted for 16 weeks on 38 men found that individuals who ingested 20 grams of grape extract per day had less blood sugar than those in normal groups.
- Research has found that resveratrol, an element found in grape skins, increases the sensitivity of insulin, which improves the glucose process in a person’s body and reduces blood sugar levels. The findings of the study revealed that resveratrol increases the number of glucose receptors on cell members, which has a beneficial effect on blood sugar.
- According to a study, there is a common belief that people suffering from diabetes should not eat grapes because they contain sugar. Diabetes UK has expressed concern that the fruit contains sugar, which increases a person’s blood glucose.
Bonus Point
If you consume grapes regularly, you will never be a victim of diabetes because grapes contain ingredients that protect you from diabetes. Grape consumption prevents the risk of metabolic syndrome, an important factor in diabetes.
Grapes regulate glucose levels in the body. It has also been proven in research that the risk of diabetes is much lower for those who consume grapes regularly. According to research, people get benefits from eating fruits rich in phytochemicals, like grapes. Diabetes patients should include fruits with vitamins, minerals, and fiber in their diet.
[Source: onlymyhealth.com]
Conclusion
You have read above that the diabetes and banana topic is helpful.
Prediabetics and diabetics can include bananas in their diet. The health benefits of bananas are great. But the sugar content of ripe bananas makes it unattractive to take in excess. Unripe bananas are even better to eat, as they contain resistant starch.
The bottom line is that all fruits, because of their sugar composition, are best consumed a little at a time.
Please let me know your contribution to the information I have shared. Kindly use the comments form.
FAQs
**Q: Can bananas be included in a diabetic diet?
A: Yes, bananas can be included in a diabetic diet. They are a good source of essential nutrients, including dietary fiber, potassium, and vitamin C. However, it’s important to consume them in moderation and consider their impact on blood sugar levels. Opt for smaller-sized bananas and monitor your blood glucose levels to determine the right portion size for you.
**Q: How do bananas affect blood sugar levels in people with diabetes?
A: Bananas have a moderate glycemic index, which means they can raise blood sugar levels. However, the glycemic response to bananas can vary depending on factors such as ripeness and the individual’s metabolism. Pairing bananas with a source of protein or healthy fat can help slow down the absorption of sugars and minimise their impact on blood glucose levels.
**Q: Are there any specific benefits of bananas for individuals with diabetes?**
A: Yes, bananas offer several benefits for individuals with diabetes. They are a good source of dietary fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve digestion. Additionally, bananas contain potassium, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure. The vitamin C content in bananas also supports immune function.
**Q: How many bananas can a person with diabetes safely consume in a day?**
A: The number of bananas a person with diabetes can safely consume in a day depends on various factors, including their individual carbohydrate tolerance and overall dietary plan. It is generally recommended to limit the intake of bananas to one medium-sized banana per serving. It’s essential to work with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion size and incorporate it into an overall balanced meal plan.
**Q: Can eating too many bananas cause a spike in blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes?**
Consuming excessive amounts of bananas can potentially cause a spike in blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes. Bananas contain natural sugars, which can impact blood glucose levels if consumed in large quantities. It’s important to be mindful of portion sizes and monitor your blood sugar levels closely to manage your carbohydrate intake effectively.
**Q: Are there any alternatives to consuming whole bananas for individuals with diabetes?**
A: Yes, there are alternatives to consuming whole bananas for individuals with diabetes. One option is to opt for smaller-sized bananas, which generally have a lower carbohydrate content. Another alternative is to incorporate sliced or mashed bananas into dishes like smoothies, oatmeal, or yoghurt. This way, you can control the portion size and combine it with other nutritious ingredients for a balanced meal or snack.
**Q: Should individuals with diabetes avoid eating bananas altogether?
A: Individuals with diabetes do not need to completely avoid eating bananas. Bananas can be a part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation and in line with an individual’s overall dietary plan. It’s important to consider personal carbohydrate tolerance, monitor blood sugar levels, and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion sizes and frequency of banana consumption.
**Q: Do bananas have any impact on insulin resistance in individuals with diabetes?
A: Bananas themselves do not have a direct impact on insulin resistance in individuals with diabetes. However, as part of a balanced diet, they can contribute to overall health and help manage blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, weight management, and a well-rounded diet, including foods like bananas, can support insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health in individuals with diabetes.
**Q: Can green bananas be included in a diabetic diet?
A: Yes, green bananas can be included in a diabetic diet. Green bananas have a lower glycemic index compared to ripe bananas, which means they have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels. They also contain resistant starch, a type of fiber that helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes digestive health. Including green bananas in your diet can be a healthy choice for managing blood glucose levels.
**Q: Are there any precautions to keep in mind when consuming bananas for individuals with diabetes?**
A: When consuming bananas, individuals with diabetes should keep a few precautions in mind. It’s important to choose ripe but not overly ripe bananas, as the latter tend to have a higher glycemic index. Additionally, it’s advisable to pair bananas with protein or healthy fat to minimise their impact on blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly and working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalised guidance for incorporating bananas into a diabetes management plan.
Very Important: Please note that all information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. They should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. So, please consult with your doctor and/or registered dietitian or nutritionist for any professional advice before applying any of the information on your health issues.



Very clear and help full explanation. Waiting more such feedback in future. Thank you.
Abraham Teclu Gebreslassie
Thanks, Abraham, my apologies for the late response!
Alexander
Thanks Abraham for your kind comments.
For sure, will keep in touch.
Stay tuned!
Alexander
Unripe banana spikes my B’s, especially when I eat it so much, this kind of worry me a lot cos people say unripe plantain is good for diabetic people but is not looking like that to me.
Hi Solomon, as you have said, many people including myself do benefit from the residual starch of unripe plantain to prevent sugar spikes when eaten. Scientific studies also mention the advantage of eating this item for diabetes control. Please discuss with your dietitian maybe you need to reduce the amount of food you consume at a time (portion control). Thanks for your comments!
This is good advice and it has helped my association of diabetics in Malawi
Glad to hear that, Emmanuel!
We need more of this information for association of diabetics in Malawi
Thank you, Emmanuel. Will do my best!
Cheers
Alexander
Thanks for your information I have learned more
Thanks, Miriam