Last Updated on February 26, 2024 by Alexander Sennuga

The diabetes complications topic deserves mention in all diabetes discussions and education.
Why so?
We already know that cases of diabetes are spreading across the earth. This is often so despite all the concerted efforts to reverse the trend. But, is preventing the spread the sole thing there is to know about the disease? In fact, not. Read on.
Also, we all know that when high blood glucose isn’t in check, it can well cause health issues. It can cause short-term, long-term, irreversible, and regrettable outcomes.
So, are there major potential complications? And if there are, can we prevent them in the first place?
This post will discuss all there is to understand about the likely complications of diabetes. Then we look at the possible preventive measures.
So, let’s dive right in…
Diabetic Complications

As expected, no one would possess the experience of diabetic complications. It’s too damaging to be the proper choice.
This is why everyone must know how to manage diabetes mellitus (DM).
They are the damages to body organs and tissues resulting from chronic diabetes. Additionally, in most cases, the damages are permanent.
Scientists classify complications into two main categories: These are microvascular complications and macrovascular complications.
Let’s see what these mean below.
Microvascular diabetic complications
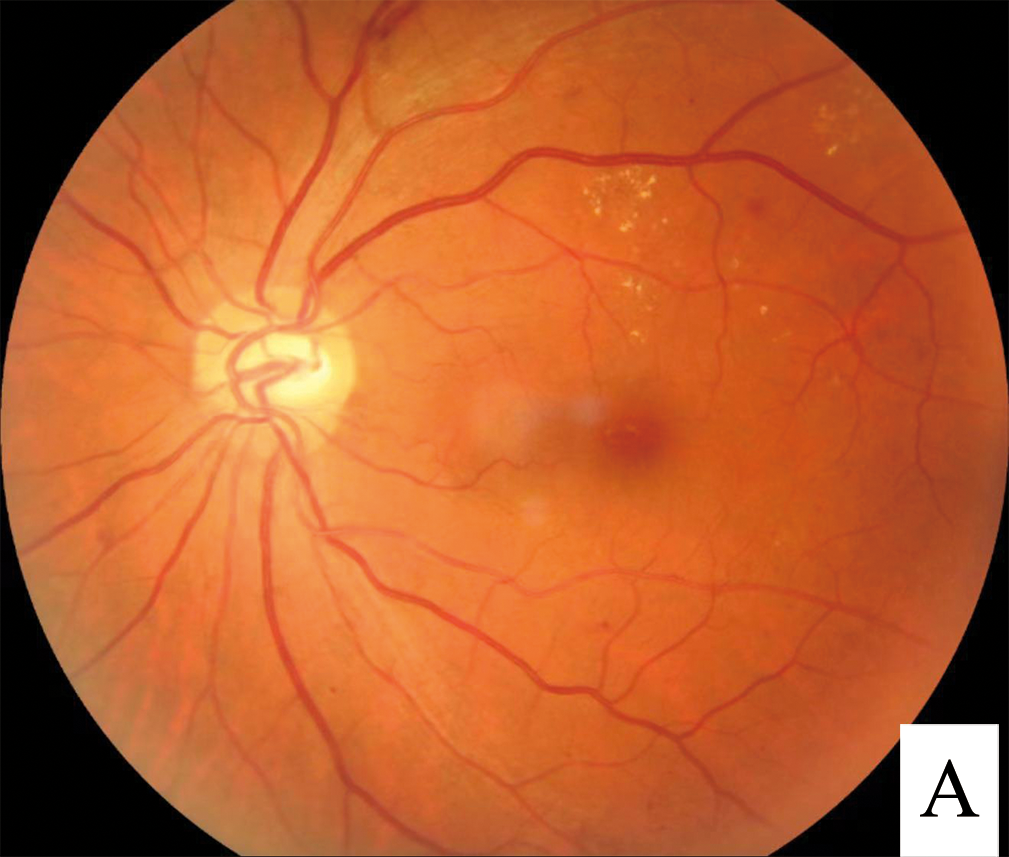
Diabetes is associated with significant microvascular complications: retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy
Diabetic retinopathy remains the most common cause of blindness in working-age adults in the developed world.
Early aggressive treatment of microalbuminuria reduces the risk of the development of nephropathy
Neuropathy may manifest in different ways and can be difficult to manage
Prevention and reduction in the progression of microvascular complications require intensive management of glucose, blood pressure, and lipids.
Macrovascular diabetic complications
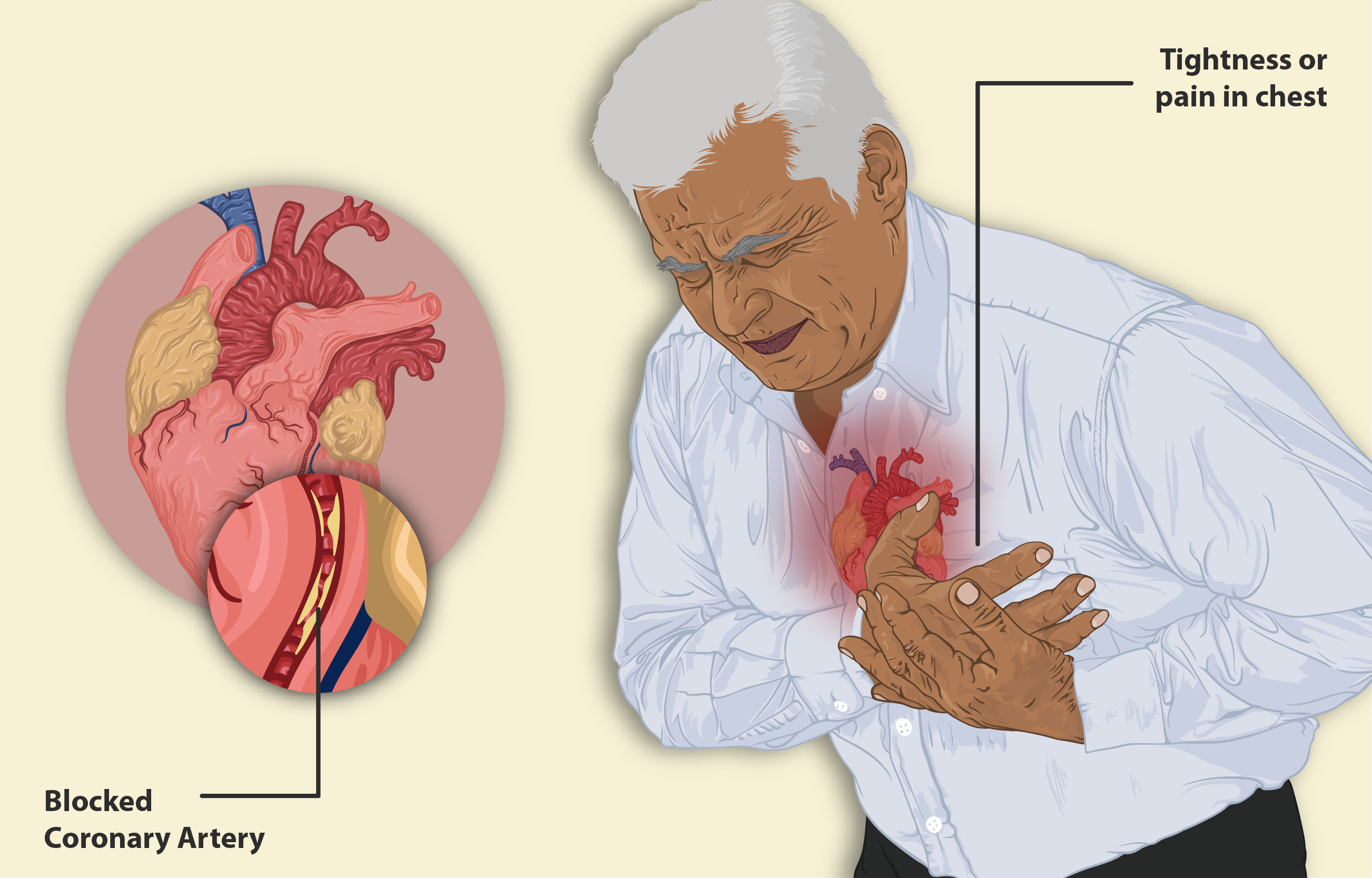
Macrovascular complications of diabetes can have long-term effects on different parts of the body. They include high blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and kidney disease.
Macrovascular disease affects the large blood vessels, including the coronary arteries, the aorta, and the large arteries in the brain and limbs. Some may appear soon after diagnosis, while others may take several years to develop.
What are the macrovascular complications of diabetes?
Macrovascular complications of diabetes can lead to the following:
If a person does not receive treatment, these complications can lead to heart failure and, ultimately, death. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source, 1 person in the United States dies from cardiovascular disease every 34 seconds.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications

If you do not manage well your type 2 diabetes but allow it to remain with you, you risk developing complications. Uncontrolled diabetes can cause damage to blood vessels, various body organs, and cells.
Here’s how these happen.
Complications in the Kidney

Prolonged and untreated type 2 diabetes can cause renal disorders. As an example, a renal disorder can cause renal failure. It’s on record that diabetes is the leading cause of renal failure.
Consistent with experts, the prevention of complications within the kidney requires controlling the comorbidities. That’s to say, we should always aim to control not only blood sugar but also vital signs and cholesterol.
Retinopathy (eye problems)

The tiny vessel is responsible for sending oxygen to the retina, which is often damaged by diabetes. This damage is called diabetic retinopathy.
Scientific studies show that it’s the leading cause of blindness in adults aged 20 to 74 years.
Diabetic neuropathy
One damage untreated diabetes for an extended period causes is nerve damage. This is called diabetic neuropathy. The damage usually affects fingers, hands, feet, and toes. The patient experiences pain, tingling, numbness, and a kind of needle/pin sensation in those parts of the body.
Unfortunately, the damage can sometimes be irreversible.
It doesn’t stop there.
In addition to the above, diabetic neuropathy can cause a significant problem in the foot.
How?
When the arteries around the feet get blocked, blood flow to the foot is reduced. Any slight injury can cause foot sores. Because there’s now almost a lifeless state on the foot, an infection can occur.
And in serious situations, it can lead to amputation.
Anything else? Yes.
Diabetic complications within the artery and heart problems
If you do not manage to control your diabetes type 2 by adopting a healthy diet and adequate exercise, this will happen to you. You are in danger of plaque buildup in your arteries, causing a decrease in blood flow.
When this happens, blood clots can occur, leading to the hardening of the arteries.
The last word result of all this is often that there’s a high chance of a heart attack or stroke.
Indeed, studies have shown that more than half of type 2 diabetes cases can cause a heart attack. This is why the patient should ensure good management of the disease.
Tooth problems thanks to high blood sugar

Diabetes type 2 complications affect your teeth and gums down the road. How? High blood sugar enables bacteria in the plaque buildup process.
When this happens, it puts him in danger for the following:
- Cavities
- Tooth decay
- Gum disease (and then tooth loss in severe cases)
Extra care becomes necessary with these problems to avoid infection setting in.
Gestational Diabetes Complications

Gestational diabetes is one type of insulin resistance that happens during pregnancy. Scientists say about 18% of pregnant women develop this disease. Although consistent with scientific facts, the disease in most cases disappears after childbirth.
Even so, there are some complications related to it. These are the following:
- The mother stands a 60% chance of developing type 2 diabetes in later life
- The baby has the potential for type 2 diabetes later
- There is the possibility of the baby being fat
- The birth of the baby is by surgical delivery (C-section)
We have discussed the complications of diabetes. Now, it is time to look into how to prevent diabetic complications. Read on.
How Can We Prevent Diabetes Complications?
Let us check out the three sorts of diabetes again in discussing complications.
Type 1 diabetes
Because of its characteristics, type 1 diabetes isn’t preventable. Therefore, to stop its complications, what you’ll do isn’t much. Ensure strict usage of your medication and adequate cooperation with your healthcare providers.
Type 2 and gestational diabetes
It is logical to mention or assume this theory without question. Any successful efforts to avoid or prevent disease will also succeed in preventing its complications.
Makes sense?
This assumption is applicable to type 2 and gestational diabetes.
All the measures to stop them apply to preventing their complications.
What, then, are the preventive strategies?
We must specialise in making 7 specific healthy choices. These are:
- Ensure strict adherence to a healthy diet
- Be prepared to shed weight if you’re overweight or obese
- Daily exercise of about 30 minutes is helpful
- Avoid stress
- Quit smoking
- Avoid or reduce alcohol consumption
- Get enough sleep every day (7-8 hours, being the standard medical advice)
What else?
Outside of the above healthy choices, the following are good practices as well:
- Regular checks of your blood glucose, vital signs, and cholesterol for correct control
- Go for your medical reviews when they are due
- Ensure you do not allow your prediabetes to reach type 2 diabetes
Conclusion
Diabetic complications aren’t what anyone would like to experience. They are damaging in the long term, and they can cause permanent disability.
Type 1 diabetes isn’t preventable. But, both type 2 and gestational diabetes are. Therefore, type 1 features a limited option to prevent complications. He needs only to make sure he uses the medication from his doctor or healthcare provider.
Preventing type 2 and gestational diabetes is straightforward. So, all the preventive measures to stop developing the diseases are enough to prevent their complications. A healthy diet and weight, adequate exercise, and the avoidance of stress are the right strategies.
Adequate sleep a day is additionally key.
FAQ
**Q: What are the most common diabetic complications?**
A: The most common complications associated with diabetes include cardiovascular disease, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic nephropathy. These complications can arise due to prolonged periods of high blood sugar levels.
**Q: How does diabetes affect the cardiovascular system?**
A: Diabetes can have a significant impact on the cardiovascular system. Individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of developing conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Individuals with diabetes must manage their blood sugar levels and adopt a healthy lifestyle to minimise these risks.
**Q: What is diabetic neuropathy?**
A: Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage that occurs as a result of diabetes. It commonly affects the legs and feet. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness. Proper blood sugar control is essential to prevent or delay the onset of diabetic neuropathy.
**Q: How does diabetes affect the eyes?**
A: Diabetes can lead to a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which affects the blood vessels in the retina. It can cause vision problems and, if left untreated, may lead to blindness. Regular eye examinations and maintaining good blood sugar control are crucial in preventing and managing diabetic retinopathy.
**Q: What is diabetic nephropathy?**
A: Diabetic nephropathy is a kidney disease that occurs as a complication of diabetes. It involves damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function. Managing blood sugar levels and blood pressure, along with a healthy lifestyle, are essential in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
**Q: Can diabetic complications be prevented?**
A: While it may not be possible to completely prevent all diabetic complications, there are steps individuals with diabetes can take to reduce their risk. These include maintaining good blood sugar control, adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and attending regular check-ups with healthcare professionals.
**Q: How can I manage diabetic complications effectively?**
A: Effective management of diabetic complications involves a comprehensive approach. It includes maintaining optimal blood sugar control, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications as directed, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and attending regular medical check-ups. Collaborating with healthcare professionals is crucial for developing an individualised management plan.
**Q: What are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent diabetic complications?**
A: Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic complications. These changes include maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco use, limiting alcohol consumption, and effectively managing stress levels.
**Q: Are all diabetic complications reversible?**
A: While some diabetic complications can be reversible, such as early stages of diabetic neuropathy or retinopathy, many complications are not entirely reversible once they have progressed. However, proper management and control of blood sugar levels can help slow down the progression of complications and minimise their impact on overall health.
**Q: Why is it important to seek medical attention for diabetic complications?**
A: Seeking medical attention for diabetic complications is crucial because timely intervention can prevent or delay the worsening of complications. Healthcare professionals can provide appropriate treatment, guidance on managing symptoms, and help develop a personalised plan to optimise overall health. Regular monitoring and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with diabetic complications.
Do you know of the other diabetic complications and their preventive measures? Please share them here in the comments section.
Very Important: Please note that all information provided on this site is for educational purposes only. They should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. So, please consult with your doctor and/or registered dietitian or nutritionist for any professional advice before applying any of the information on your health issues.

